描述用户界面
React 是一个用于渲染用户界面 (UI) 的 JavaScript 库。UI 由按钮、文本和图片等小单元构建而成。React 允许你将它们组合成可重用、可嵌套的组件。从网站到手机应用,屏幕上的所有内容都可以分解为组件。在本章中,你将学习创建、自定义和有条件地显示 React 组件。
¥React is a JavaScript library for rendering user interfaces (UI). UI is built from small units like buttons, text, and images. React lets you combine them into reusable, nestable components. From web sites to phone apps, everything on the screen can be broken down into components. In this chapter, you’ll learn to create, customize, and conditionally display React components.
在此章节中
你的第一个组件
¥Your first component
React 应用是由称为组件的独立 UI 部分构建的。React 组件是一个 JavaScript 函数,你可以在其中添加标记。组件可以小到一个按钮,也可以大到整个页面。这是渲染三个 Profile 组件的 Gallery 组件:
¥React applications are built from isolated pieces of UI called components. A React component is a JavaScript function that you can sprinkle with markup. Components can be as small as a button, or as large as an entire page. Here is a Gallery component rendering three Profile components:
function Profile() { return ( <img src="https://i.imgur.com/MK3eW3As.jpg" alt="Katherine Johnson" /> ); } export default function Gallery() { return ( <section> <h1>Amazing scientists</h1> <Profile /> <Profile /> <Profile /> </section> ); }
准备好学习这个主题了吗?
阅读 你的第一个组件 以了解如何声明和使用 React 组件。
¥Read Your First Component to learn how to declare and use React components.
阅读更多导入和导出组件
¥Importing and exporting components
你可以在一个文件中声明多个组件,但大文件可能难以导航。要解决这个问题,你可以将一个组件导出到它自己的文件中,然后从另一个文件中导入该组件:
¥You can declare many components in one file, but large files can get difficult to navigate. To solve this, you can export a component into its own file, and then import that component from another file:
import Profile from './Profile.js'; export default function Gallery() { return ( <section> <h1>Amazing scientists</h1> <Profile /> <Profile /> <Profile /> </section> ); }
准备好学习这个主题了吗?
阅读 导入和导出组件 以了解如何将组件拆分到它们自己的文件中。
¥Read Importing and Exporting Components to learn how to split components into their own files.
阅读更多使用 JSX 编写标记
¥Writing markup with JSX
每个 React 组件都是一个 JavaScript 函数,其中可能包含 React 渲染到浏览器中的一些标记。React 组件使用称为 JSX 的语法扩展来表示该标记。JSX 看起来很像 HTML,但更严格一些,并且可以显示动态信息。
¥Each React component is a JavaScript function that may contain some markup that React renders into the browser. React components use a syntax extension called JSX to represent that markup. JSX looks a lot like HTML, but it is a bit stricter and can display dynamic information.
如果我们将现有的 HTML 标记粘贴到 React 组件中,它并不总是有效:
¥If we paste existing HTML markup into a React component, it won’t always work:
export default function TodoList() { return ( // This doesn't quite work! <h1>Hedy Lamarr's Todos</h1> <img src="https://i.imgur.com/yXOvdOSs.jpg" alt="Hedy Lamarr" class="photo" > <ul> <li>Invent new traffic lights <li>Rehearse a movie scene <li>Improve spectrum technology </ul>
如果你有这样的现有 HTML,你可以使用 转换器 修复它:
¥If you have existing HTML like this, you can fix it using a converter:
export default function TodoList() { return ( <> <h1>Hedy Lamarr's Todos</h1> <img src="https://i.imgur.com/yXOvdOSs.jpg" alt="Hedy Lamarr" className="photo" /> <ul> <li>Invent new traffic lights</li> <li>Rehearse a movie scene</li> <li>Improve spectrum technology</li> </ul> </> ); }
准备好学习这个主题了吗?
阅读 使用 JSX 编写标记 以了解如何编写有效的 JSX。
¥Read Writing Markup with JSX to learn how to write valid JSX.
阅读更多JSX 中使用大括号的 JavaScript
¥JavaScript in JSX with curly braces
JSX 允许你在 JavaScript 文件中编写类似 HTML 的标记,将渲染逻辑和内容保持在同一位置。有时你会希望在该标记内添加一些 JavaScript 逻辑或引用动态属性。在这种情况下,你可以在 JSX 中使用大括号 “打开一扇窗” 到 JavaScript:
¥JSX lets you write HTML-like markup inside a JavaScript file, keeping rendering logic and content in the same place. Sometimes you will want to add a little JavaScript logic or reference a dynamic property inside that markup. In this situation, you can use curly braces in your JSX to “open a window” to JavaScript:
const person = { name: 'Gregorio Y. Zara', theme: { backgroundColor: 'black', color: 'pink' } }; export default function TodoList() { return ( <div style={person.theme}> <h1>{person.name}'s Todos</h1> <img className="avatar" src="https://i.imgur.com/7vQD0fPs.jpg" alt="Gregorio Y. Zara" /> <ul> <li>Improve the videophone</li> <li>Prepare aeronautics lectures</li> <li>Work on the alcohol-fuelled engine</li> </ul> </div> ); }
准备好学习这个主题了吗?
阅读 JSX 中使用大括号的 JavaScript 以了解如何从 JSX 访问 JavaScript 数据。
¥Read JavaScript in JSX with Curly Braces to learn how to access JavaScript data from JSX.
阅读更多将属性传递给组件
¥Passing props to a component
React 组件使用属性相互通信。每个父组件都可以通过给它们属性将一些信息传递给它的子组件。属性可能会让你想起 HTML 属性,但你可以通过它们传递任何 JavaScript 值,包括对象、数组、函数,甚至 JSX!
¥React components use props to communicate with each other. Every parent component can pass some information to its child components by giving them props. Props might remind you of HTML attributes, but you can pass any JavaScript value through them, including objects, arrays, functions, and even JSX!
import { getImageUrl } from './utils.js' export default function Profile() { return ( <Card> <Avatar size={100} person={{ name: 'Katsuko Saruhashi', imageId: 'YfeOqp2' }} /> </Card> ); } function Avatar({ person, size }) { return ( <img className="avatar" src={getImageUrl(person)} alt={person.name} width={size} height={size} /> ); } function Card({ children }) { return ( <div className="card"> {children} </div> ); }
准备好学习这个主题了吗?
阅读 将属性传递给组件 以了解如何传递和读取属性。
¥Read Passing Props to a Component to learn how to pass and read props.
阅读更多条件渲染
¥Conditional rendering
你的组件通常需要根据不同的条件显示不同的内容。在 React 中,你可以使用 if 语句、&& 和 ? : 运算符等 JavaScript 语法有条件地渲染 JSX。
¥Your components will often need to display different things depending on different conditions. In React, you can conditionally render JSX using JavaScript syntax like if statements, &&, and ? : operators.
在此示例中,JavaScript && 运算符用于有条件地渲染复选标记:
¥In this example, the JavaScript && operator is used to conditionally render a checkmark:
function Item({ name, isPacked }) { return ( <li className="item"> {name} {isPacked && '✅'} </li> ); } export default function PackingList() { return ( <section> <h1>Sally Ride's Packing List</h1> <ul> <Item isPacked={true} name="Space suit" /> <Item isPacked={true} name="Helmet with a golden leaf" /> <Item isPacked={false} name="Photo of Tam" /> </ul> </section> ); }
准备好学习这个主题了吗?
阅读 条件渲染 以了解有条件地渲染内容的不同方式。
¥Read Conditional Rendering to learn the different ways to render content conditionally.
阅读更多渲染列表
¥Rendering lists
你通常希望显示数据集合中的多个相似组件。你可以将 JavaScript 的 filter() 和 map() 与 React 结合使用,以过滤数据数组并将其转换为组件数组。
¥You will often want to display multiple similar components from a collection of data. You can use JavaScript’s filter() and map() with React to filter and transform your array of data into an array of components.
对于每个数组项,你需要指定一个 key。通常,你会希望使用数据库中的 ID 作为 key。键让 React 跟踪每个条目在列表中的位置,即使列表发生变化也是如此。
¥For each array item, you will need to specify a key. Usually, you will want to use an ID from the database as a key. Keys let React keep track of each item’s place in the list even if the list changes.
import { people } from './data.js'; import { getImageUrl } from './utils.js'; export default function List() { const listItems = people.map(person => <li key={person.id}> <img src={getImageUrl(person)} alt={person.name} /> <p> <b>{person.name}:</b> {' ' + person.profession + ' '} known for {person.accomplishment} </p> </li> ); return ( <article> <h1>Scientists</h1> <ul>{listItems}</ul> </article> ); }
准备好学习这个主题了吗?
阅读 渲染列表 以了解如何渲染组件列表以及如何选择键。
¥Read Rendering Lists to learn how to render a list of components, and how to choose a key.
阅读更多保持组件纯粹
¥Keeping components pure
有些 JavaScript 函数是纯函数。纯函数:
¥Some JavaScript functions are pure. A pure function:
-
管好自己的事。它不会更改调用之前存在的任何对象或变量。
¥Minds its own business. It does not change any objects or variables that existed before it was called.
-
相同的输入,相同的输出。给定相同的输入,纯函数应该总是返回相同的结果。
¥Same inputs, same output. Given the same inputs, a pure function should always return the same result.
通过严格地将你的组件编写为纯函数,你可以在代码库增长时避免一整类令人困惑的错误和不可预测的行为。这是一个不纯组件的例子:
¥By strictly only writing your components as pure functions, you can avoid an entire class of baffling bugs and unpredictable behavior as your codebase grows. Here is an example of an impure component:
let guest = 0; function Cup() { // Bad: changing a preexisting variable! guest = guest + 1; return <h2>Tea cup for guest #{guest}</h2>; } export default function TeaSet() { return ( <> <Cup /> <Cup /> <Cup /> </> ); }
你可以通过传递一个属性而不是修改一个预先存在的变量来使这个组件变得纯粹:
¥You can make this component pure by passing a prop instead of modifying a preexisting variable:
function Cup({ guest }) { return <h2>Tea cup for guest #{guest}</h2>; } export default function TeaSet() { return ( <> <Cup guest={1} /> <Cup guest={2} /> <Cup guest={3} /> </> ); }
准备好学习这个主题了吗?
阅读 保持组件纯粹 以了解如何将组件编写为纯粹的、可预测的函数。
¥Read Keeping Components Pure to learn how to write components as pure, predictable functions.
阅读更多你的用户界面就像一棵树
¥Your UI as a tree
React 使用树来建模组件和模块之间的关系。
¥React uses trees to model the relationships between components and modules.
React 渲染树是组件之间父子关系的表示。
¥A React render tree is a representation of the parent and child relationship between components.
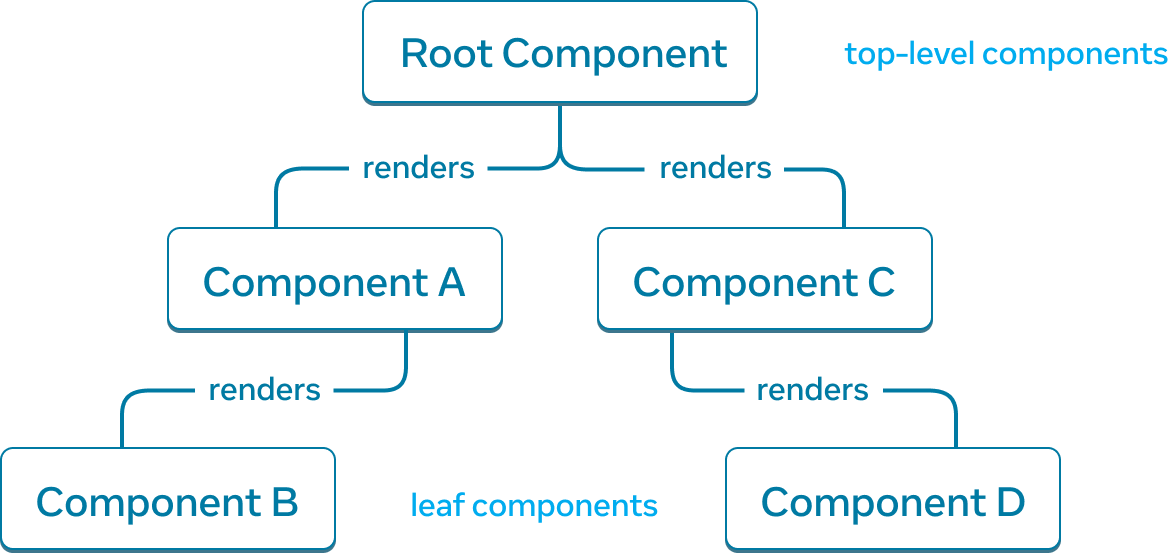
靠近树顶部、靠近根组件的组件被视为顶层组件。没有子组件的组件是叶组件。这种组件分类对于理解数据流和渲染性能很有用。
¥Components near the top of the tree, near the root component, are considered top-level components. Components with no child components are leaf components. This categorization of components is useful for understanding data flow and rendering performance.
对 JavaScript 模块之间的关系进行建模是了解应用的另一种有用方法。我们将其称为模块依赖树。
¥Modelling the relationship between JavaScript modules is another useful way to understand your app. We refer to it as a module dependency tree.
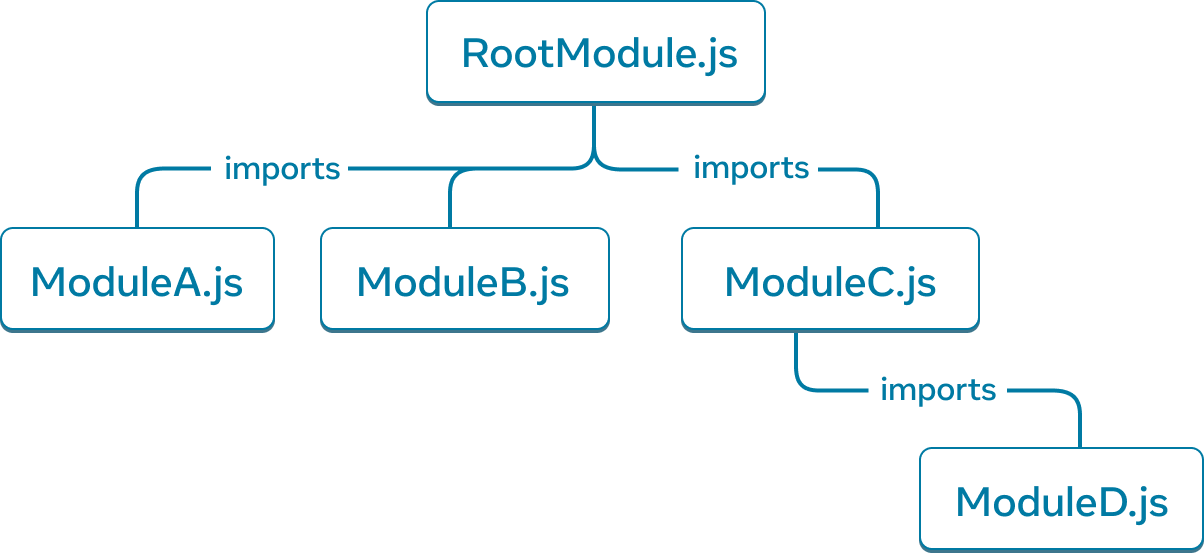
构建工具经常使用依赖树来打包所有相关的 JavaScript 代码,以供客户端下载和渲染。较大的包大小会降低 React 应用的用户体验。了解模块依赖树有助于调试此类问题。
¥A dependency tree is often used by build tools to bundle all the relevant JavaScript code for the client to download and render. A large bundle size regresses user experience for React apps. Understanding the module dependency tree is helpful to debug such issues.
准备好学习这个主题了吗?
阅读 你的用户界面就像一棵树 了解如何为 React 应用创建渲染和模块依赖树,以及它们如何成为改善用户体验和性能的有用心理模型。
¥Read Your UI as a Tree to learn how to create a render and module dependency trees for a React app and how they’re useful mental models for improving user experience and performance.
阅读更多下一步是什么?
¥What’s next?
前往 你的第一个组件 开始逐页阅读本章!
¥Head over to Your First Component to start reading this chapter page by page!
或者,如果你已经熟悉这些主题,为什么不阅读 添加交互性?
¥Or, if you’re already familiar with these topics, why not read about Adding Interactivity?